A long sand body more or less parallel with a shoreline but separated from it by a lagoon:a
delta d. tidal flat
b. barrier island e. varve
c. drift
B
You might also like to view...
Colonialism always results in ________ domination of a foreign society by the colonizing power
A) political B) legal C) religious D) cultural E) both political and legal
Using Map T-1, the “Hawaii, Hawaii,” topographic map (scale 1:250,000; contour interval 200 feet), calculate the gradient of Mauna Loa (19°28'17"N, 155°35'41"W) along line AB, from the 5000', contour (near Point A) toward the summit. On the edge of a piece of paper measure out a distance of 10 miles using the graphic map scale, and then determine the elevation change over that distance.
In this problem, you will compute the gradients of Mauna Loa in Hawai‘i, Mount Vsevidof in Alaska, and SP Mountain in Arizona. (You may also determine the elevation changes and distances needed to calculate these gradients by using Google Earth™.) The recommended starting point and distance to measure are given for all three volcanoes.
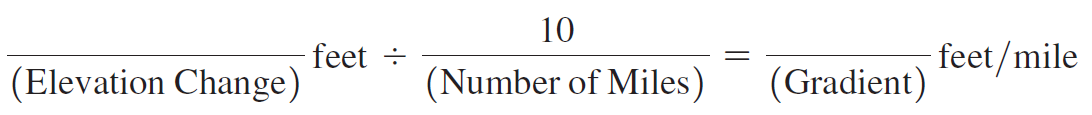
Smoking contributes to the risk of all of the following, except
A) lung cancer. B) heart disease. C) COPD and other related lung diseases. D) malaria and tuberculosis.
Physical geography's major function is to study and learn about:
a. human activity and the results thereof.
b. Earth's environments and the processes that influence them.
c. the physical and human features of a region.
d. the composition of Earth's crust.