In New York, a welfare recipient can earn $90 per month without having her benefits reduced. Beyond $90, benefits are reduced by 57 cents for every dollar of earnings. Consider Jackie, a resident of New York, who can earn $10 per hour. If she does not work at all, she is eligible for welfare benefits of $577.
(A) If she works 10 hours, how much are her work earnings, how much is her welfare benefits,
and how much is her total income?
(B) After Jackie works a certain number of hours, she does not receive any benefits at all.
What is that number of hours?
(A) If Jackie works 10 hours at $10 per hour, she will have earned $100 from working. She
gets to earn $90 before her benefits are reduced. She earned $10 over that limit, so her
benefits will be reduced to 577 - (0.57 * 10) = 571.3. She will have received in total $671.3.
(B) She would need to work 110.228 hours before benefits are completely eliminated.
You might also like to view...
The most important factor contributing to wage differences in the labor market is differences in the level of education and training among workers
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The greater the degree of specialization in the economy, the: a. easier it is to discover a double coincidence of wants
b. more feasible is a barter system. c. less likely it is that monetary exchange will develop. d. harder it is to negotiate an exchange rate between all pairs of goods. e. more likely it is that individual consumers are self-sufficient.
Which requirement for perfect competition rules out trade associations or other collusive arrangements in which firms work together to influence price?
a. Freedom of entry and exit. b. Homogeneity of product. c. Perfect information. d. Numerous small firms and customers.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 15.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow. Below are cost curves for Dom's Barber Shop, a monopolistically competitive firm. 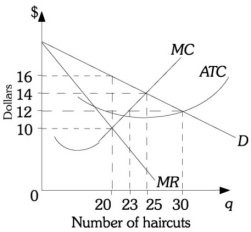 Figure 15.1 Refer to Figure 15.1. From society's point of view, the ________ level is 25 haircuts.
Figure 15.1 Refer to Figure 15.1. From society's point of view, the ________ level is 25 haircuts.
A. shut down B. efficient output C. minimum output D. monopoly output