Consider the following:
(i) Suppose Laurent has $60 per week to spend on food and clothing. The price of food is $4 per unit, and the price of clothing is $6 per unit. Sketch Laurent's budget line on the axes provided.
(ii) Laurent applies to the local government for food stamps and is given $40 worth of food stamps per week. On the axes, show how the receipt of food stamps affects Laurent's budget line.
(iii) Suppose that instead of food stamps, Laurent receives $40 in cash per week from a relative. On the axes, show how this gift affects Laurent's budget line.
(iv) Add appropriate indifference curves to the diagram to show that a gift of $40 in cash could make Laurent better off than the receipt of $40 in food stamps.
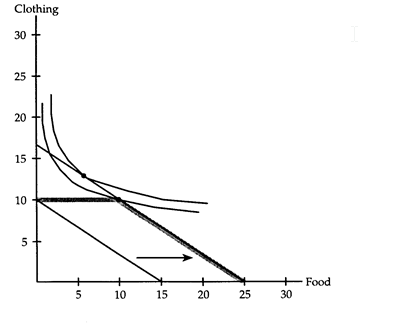
(i) The budget line will have a horizontal intercept of 15 and a vertical intercept of 10.
(ii) The food stamps cause the budget line to shift 10 units to the right.
(iii) With the cash gift, the budget line has a horizontal intercept 25 and a vertical intercept of 16 2/3.
(iv) Laurent will be better off with the cash gift if his optimum under the cash gift contains more than 10 units of clothing and less than 10 units of food. This situation is shown in the accompanying diagram.
You might also like to view...
To achieve long-run equilibrium in an economy with a recessionary gap, without the use of stabilization policy, the inflation rate must:
A. not change. B. increase. C. decrease. D. either increase or decrease depending on the relative shifts of AD and AS.
A low correlation coefficient implies that
A) the line always has a flat slope B) in the scatterplot, the points fall quite far away from the line C) the two variables are unrelated D) you should use a tighter scale of the vertical and horizontal axis to bring the observations closer to the line
When there is a recessionary gap, inflation will ________, in response to which the Federal Reserve will ________ real interest rates, and output will ________.
A. decline; lower; decline B. increase; raise; decline C. decline; lower; expand D. decline; raise; decline
Argentina in 2001 faced a debt problem more serious than the U.S. debt problem because Argentina was obligated to repay its debt in
A. U.S. dollars. B. their own currencies. C. a relatively short period of time. D. large installments.