The logic of why international trade increases well-being is
a. a major revision of the logic of why trade within a country increases well-being.
b. completely different from the logic of why trade within a country increases well-being.
c. a narrow, special case of the logic of why trade within a country increases well-being.
d. no different from the logic of why trade within a country increases well-being.
d
You might also like to view...
Use the following graph, which shows the market for euros, to answer the next question.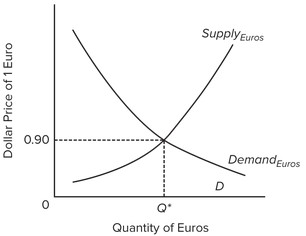 Assume the U.S. and European governments adopt a system of flexible exchange rates. If more people in Europe decide to purchase U.S. cars, what effect will this have on the market for euros?
Assume the U.S. and European governments adopt a system of flexible exchange rates. If more people in Europe decide to purchase U.S. cars, what effect will this have on the market for euros?
A. The supply of euros will decrease. B. The supply of euros will increase. C. The demand for euros will decrease. D. The demand for euros will increase.
________ analysis by economists refers to the attempt to answer questions such as what are the effects of a tax on production and consumption decisions
A) Positive B) Negative C) Normative D) Investigative
When one side of a market knows more about a product than the other side, the moral hazard problem is experienced
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Average product of labor is calculated as
A. (total product) x (total units of labor). B. (marginal product) / (total product). C. (total units of labor) / (total product). D. (total product) / (total units of labor).