When choosing between fair price and marginal cost regulation for a natural monopoly, regulators must choose between
a. c and d
b. c and e
c. two different price and quantity combinations
d. efficiency and equity
e. possible cost drift and subsidization
B
You might also like to view...
A $10 million increase in government spending has the same economic impact as a $10 million tax cut
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Jupiter likes moons more than rings and gets marginal utility worth $5 from the last moon, and $2 from the last ring. Saturn prefers rings, getting MU = $3 from the last ring and $1 from moons. Describe a trade that would increase efficiency.
What will be an ideal response?
Negative externality describes costs that include both the private costs incurred by firms and also the costs incurred by third parties outside the production process
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow.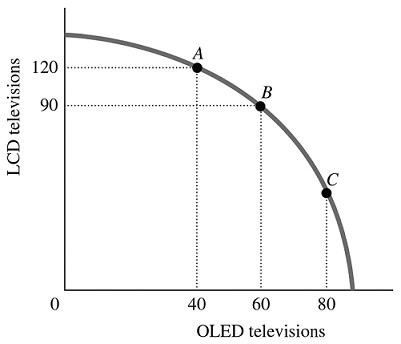 Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The economy is currently at Point A. The opportunity cost of moving from Point A to Point B is the
Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The economy is currently at Point A. The opportunity cost of moving from Point A to Point B is the
A. 30 LCD televisions that must be forgone to produce 60 additional OLED televisions. B. 90 LCD televisions that must be forgone to produce 20 additional OLED televisions. C. 30 LCD televisions that must be forgone to produce 20 additional OLED televisions. D. 120 LCD televisions that must be forgone to produce 40 additional OLED televisions.