Assume that policy makers are pursuing a fixed exchange rate regime. Now suppose that the foreign interest rate falls. Discuss what policy makers must do to maintain the pegged exchange rate. Also discuss what effect this will have on domestic output and net exports
What will be an ideal response?
If i* falls, there will be pressure on the domestic currency to appreciate. To prevent this, the domestic central bank must reduce its interest rate so that it falls by the same amount as i*. In this case, the LM curve will shift down so that the new equilibrium interest rate is equal to the now lower foreign interest rate. As i falls, E does not change. However, I will rise causing an increase in demand and output. As Y rises, imports will rise and NX will decrease.
You might also like to view...
There is no elasticity of substitution that is inconsistent with tastes being homothetic.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
When the government implements a price support program:
A. it may end up buying a lot of the good, for which it has little or no use. B. the goal is to increase the market price of the good. C. the deadweight loss created can be larger than that created by a price floor. D. All of these occur as a result of a price support program.
In a very basic principal-agent model, output is contractible if:
A. the employee works independently and cannot game the performance measure. B. the employee works in a team C. it can be observed with some positive cost. D. the employee produces many products.
Refer to the table. As compared to production alternative D, the choice of alternative C would:
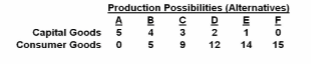
Answer the question on the basis of the data given in the following production possibilities
table:
A. tend to generate a more rapid growth rate.
B. be unattainable.
C. entail unemployment.
D. tend to generate a slower growth rate.