When very few substitutes for a good exist, demand will be
A) elastic.
B) unit-elastic.
C) inelastic.
D) perfectly elastic.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
When a government changes the official exchange rate target in a fixed exchange regime, there is a danger of
A) realignment pain. B) systemic risk. C) crowding out. D) a beggar-thy-neighbor effect.
The international trade of goods within the same industry is called
a. inter-industry trade. b. intra-industry trade. c. splitting up the value chain. c. splitting up the supply chain.
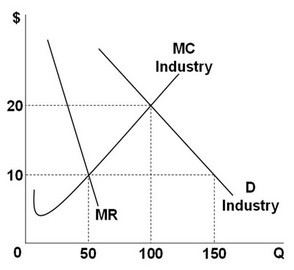 Based on the diagram above, what is the difference between the purely competitive level of output and the pure monopolist level of output?
Based on the diagram above, what is the difference between the purely competitive level of output and the pure monopolist level of output?
A. 50 units of output B. 100 units of output C. 10 units of output D. 20 units of output
If the price of hand calculators falls from $10 to $9 and, as a result, the quantity demanded increases from 100 to 125, then:
A. demand is elastic. B. demand is inelastic. C. demand is of unit elasticity. D. not enough information is given to make a statement about elasticity.