A SNP that changes the amino acid sequence of an encoded protein is termed
A) synonymous.
B) nonsynonymous.
C) transliteral.
D) mutagenic.
B) nonsynonymous.
You might also like to view...
At what step in meiosis do the daughter cells become haploid?
A. metaphase 2 B. anaphase 1 C. anaphase 2 D. prophase 2
GGG and GGC are codons for the amino acid, glycine. A mutation caused the insertion of a cytosine in place of the guanine during DNA replication. Over many generations the DNA changes so that the frequency of GGC is similar to that of GGG. What is this phenomenon called?
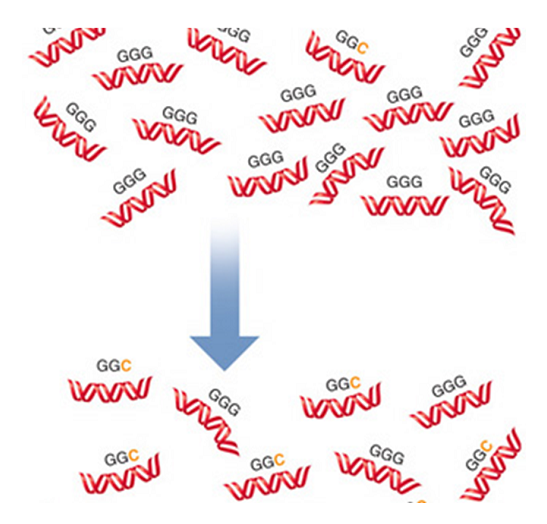
A. directional selection
B. bottleneck effect
C. stabilizing selection
D. adaptive variation
E. neutral variation
In which of the three vertical intertidal zones is biodiversity the highest, and why?
What will be an ideal response?
Why do geneticists refer to the two sugar phosphate strands of DNA as "antiparallel"?
What will be an ideal response?