The monopolist's outcome happens at a:
A. cost that is equal to a perfectly competitive one.
B. lower price than the perfectly competitive one.
C. lower quantity than the perfectly competitive one.
D. higher quantity than the perfectly competitive one.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
If property taxes were increased in a city, what would be the most likely effect on residential rents after two or three months? They would probably
A) fall. B) rise in proportion to taxes. C) rise more than in proportion to taxes. D) stay roughly unchanged.
A critical assumption in the model of demand and supply is the independence of demand and supply curves. If the two are not independent, a shift in the supply curve can lead to a shift in the demand curve referred to as
a. supply-side economics. b. supplier-induced demand. c. supply shocks. d. ceteris paribus. e. the fallacy of supply.
An example of a price floor is
a. the regulation of gasoline prices in the U.S. in the 1970s. b. rent control. c. the minimum wage. d. any restriction on price that leads to a shortage.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 23.3 below to answer the question(s) that follow.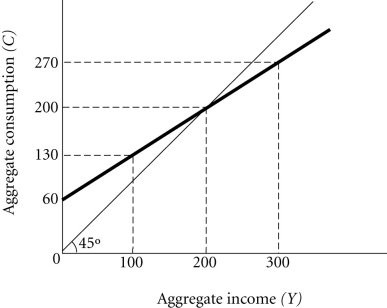 Figure 23.3Refer to Figure 23.3. Aggregate saving is $240 if aggregate income is
Figure 23.3Refer to Figure 23.3. Aggregate saving is $240 if aggregate income is
A. $300. B. $500. C. $800. D. $1,000.