Describe two experiments that provide evidence of space-time curvature by the presence of a mass
What will be an ideal response?
Two key experiments confirmed that space-time can be curved the presence of a mass: the advance of perihelion of Mercury's orbit and the motion of light near the Sun.
Each time Mercury returns to perihelion, its closest point to the Sun, it is about 29 km (18 mi) past the position predicted by Newton's laws. This is such a small distance compared with the planet's diameter of 4880 km that it could never have been detected had it not been cumulative. Each orbit, Mercury gains only 29 km, but in a century it's ahead by over 12,000 km—more than twice its own diameter. To remedy this difference, he first calculated how much the Sun's mass curves space-time in the region of Mercury's orbit and then he calculated how Mercury moves through the space-time. The theory predicted that the curved space-time should cause Mercury's orbit to advance by 43.03 arc seconds per century, well within the range of uncertainty in the observed excess. His theory matched Newton's observations.
A second test of general relativity was related to the motion of light through the curved space-time near the Sun. Because light has a limited speed, Newton's laws predict that the gravity of an object should slightly bend the paths of light beams passing nearby. The equations of general relativity indicated that light should have an extra deflection caused by traveling through curved space-time, just as a rolling golf ball is deflected by undulations in a putting green. Einstein predicted that starlight grazing the Sun's surface would be deflected by 1.75 arc seconds, twice the deflection that Newton's law of gravity would predict. Starlight passing near the Sun is normally lost in the Sun's glare, but during a total solar eclipse, stars beyond the Sun can be seen. During the next solar eclipse, measurements were taken and they matched his predictions.
You might also like to view...
Faraday's Law: A bar magnet is pushed through a coil of wire of cross-sectional area 0.020 m2 as shown in the figure. The coil has seven turns, and the rate of change of the strength of the magnetic field in it due to the motion of the bar magnet is 0.040 T/s. What is the magnitude of the induced emf in that coil of wire?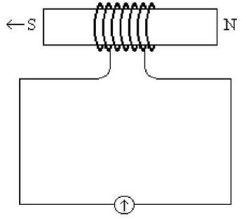
A. 5.6 × 10-3 V B. 5.6 × 10-2 V C. 5.6 × 10-1 V D. 5.6 × 10-4 V E. 5.6 × 10-5 V
____________________ clusters of galaxies contain closely spaced galaxies and often contain giant elliptical galaxies and a hot intergalactic medium
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
The Paschen series of hydrogen corresponds to electron transitions from higher levels to n = 3 . What is the shortest wavelength in that series? (R = 1.097 × 10^7 m?1 and 1 nm = 10?9 m)
a. 1875 nm b. 820 nm c. 1580 nm d. 656 nm e. 1094 nm
What is the ratio of the power levels of two sounds with intensity levels of 40. dB and 70. dB?
What will be an ideal response?