Graphically illustrate the intended effect of this tax incentive, and explain the expected outcome of phasing it out. (Assume there is no production externality.)
To promote cleaner air, the federal government in the United States enacted tax incentives for purchasing new electric vehicles or clean-fuel vehicles. These were scheduled to be phased out over time.
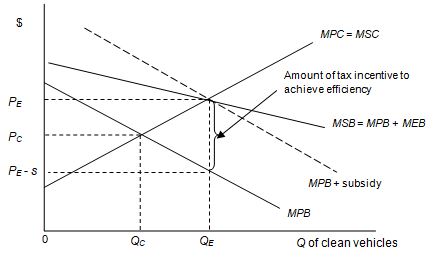
The tax incentive is offered to consumers. Therefore, it can be modeled as a subsidy (s) aimed at internalizing the positive externality of driving more environmentally friendly cars. If s is set equal to the MEB at QE, an efficient solution is achieved.
Effectively, the incentive causes the MPB to shift up by the dollar amount of the subsidy. As this occurs, the equilibrium quantity rises, and, while the efficient price is higher, the effective price to the consumer (PE – s) falls. As the tax incentive is phased out, the size of the subsidy is decreased, the MPB shifts back down, and the effective price rises.
You might also like to view...
In the figure above, originally the apartment rental market is in short-run and long-run equilibrium with a rent of $600 per month. Then the government imposes a rent ceiling of $500 per month. The deadweight loss is borne by
A) the producers only. B) the consumers only. C) all producers and some consumers. D) all consumers and some producers.
The general public has strong incentives to be informed about regulations that impact them
a. True b. False
Which of the following is a characteristic of most offshore financial centers?
A) strict domestic regulation B) minimal banking activities C) large foreign currency markets D) nominal or non-existent tax rates
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.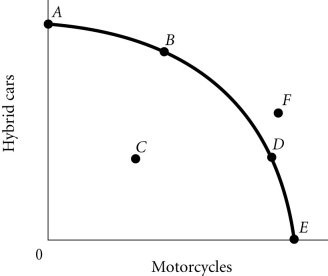 Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, as the economy moves from Point A to Point E, the opportunity cost of motorcycles, measured in terms of hybrid cars
Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, as the economy moves from Point A to Point E, the opportunity cost of motorcycles, measured in terms of hybrid cars
A. remains constant. B. decreases. C. initially increases, then decreases. D. increases.