List four objectives of workers' compensation
What will be an ideal response?
Replacement of Income
Employees injured on the job lose income if they are unable to work. For this reason, workers' compensation is intended to replace the lost income adequately and promptly. Adequate income replacement is viewed as replacement of current and future income (minus taxes) at a ratio of two-thirds (in most states). Workers' compensation benefits are required to continue even if the employer goes out of business.
Rehabilitation of the Injured Employee
A basic premise of workers' compensation is that the injured worker will return to work in every case possible, although not necessarily in the same job or career field. For this reason, a major objective of workers' compensation is to rehabilitate the injured employee. The rehabilitation program is to provide the needed medical care at no cost to the injured employee until he or she is pronounced fit to return to work. The program also provides vocational training or retraining as needed. Both components seek to motivate the employee to return to the labor force as soon as possible.
Accident Prevention
Preventing future accidents is a major objective of workers' compensation. The theory underlying this objective is that employers will invest in accident prevention programs to hold down compensation costs. The payoff to employers comes in the form of lower insurance premiums that result from fewer accidents (theoretically).
Cost Allocation
The potential risks associated with different occupations vary. For example, working as a roofer is generally considered more hazardous than working as an architect. The underlying principle of cost allocation is to spread the cost of workers' compensation appropriately and proportionately among industries ranging from the most to the least hazardous. The costs of accidents should be allocated in accordance with the accident history of the industry so that high-risk industries pay higher workers' compensation insurance premiums than do low-risk industries. Construction is a high-risk industry.
You might also like to view...
What is the longest the channel can be cut, in inches?
Reduce all fractions to their simplest forms. Convert all improper fractions to mixed numbers. Provide answers in the following format:
Fraction: 3/4
Mixed number: 1 5/8

How many sheets of standard notebook paper (8.5 in x 11 in) would it take to cover a football field (50 yards x 120 yards)?
What will be an ideal response?
In Manual J, fenestration means:
A) The material used to seal around openings. B) A barrier against infiltration. C) Anything that light can pass through. D) Openings made in the building envelope for the purpose of providing ventilation.
A solenoid having a cross section of 10 cm2 is shown in Figure P18.42.
a. Calculate the force exerted on the plunger when the distance x is 2 cm and the current in the coil (where N = 100 turns) is 5 A. Assume that the fringing and leakage effects are negligible. The relative permeabilities of the magnetic material and the non-magnetic sleeve are 2,000 and 1.
b. Develop a set of differential equations governing the behavior of the solenoid.
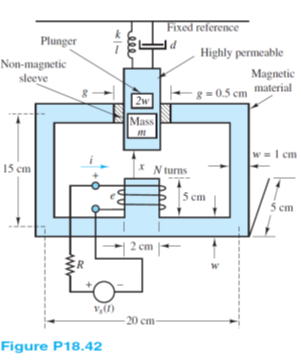
Find:
a. The force exerted on the plunger when the distance x is 2cm and the current is 5 A. Relative permeabilities of the magnetic material and the nonmagnetic sleeve are and .
b. Develop a set of differential equations governing the behavior of the solenoid.
Assumptions:
The fringing and leakage effects are negligible.