The optimal level of pollution is
a. zero
b. the level at which the marginal social cost of air quality equals the marginal social benefit
c. the level at which the average social cost of air quality equals the average social benefit
d. the level at which the total social cost of air quality equals the total social benefit
e. the level at which the marginal social cost of air quality is minimized
B
You might also like to view...
Marginal cost is the
a. change in total cost resulting from producing one more unit of output. b. change in total fixed cost resulting from producing one more unit of output. c. total cost when one more unit of output is produced. d. total fixed cost when one more unit of output is produced.
At the equilibrium price, deadweight loss is:
a. minimized. b. zero. c. maximized. d. equal to the equilibrium price multiplied by the quantity exchanged.
Cooperative equilibriums:
A. can arise if a game is repeated. B. are impossible to reach in real life. C. never result in positive-positive outcomes. D. never occur unless players act in their own self-interest.
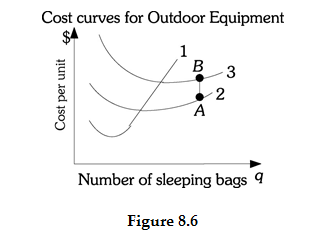
Refer to Figure 8.6. The vertical distance AB is Outdoor Equipment's A) marginal cost. B) average fixed cost. C) total fixed cost. D) total cost.