If the price of the capital intensive product rises more than does the price of the land intensive product, then
A) the relative price of the capital intensive product will fall to some point between the pretrade relative prices.
B) demand will shift away from the capital-intensive product, and its production will decrease.
C) demand will shift away from the capital-intensive product, and its production will decrease relative to that of the land intensive product.
D) the production of the capital-intensive product will decrease, but by less than production of the land-intensive product.
E) the country that exports the capital-intensive good will lose its comparative advantage.
A
You might also like to view...
Jacob buys less soda when the price of soda rises 10 percent, while the prices of all other goods also rise 10 percent. Jacob is
A) behaving in accordance with classical economic theory. B) worrying too much about a coming recession. C) suffering from money illusion. D) paying too much attention to changes in relative prices.
A chain-weighted index
A) calculates changes in prices by using an average of base years from neighboring years to obtain a more accurate measure of real GDP growth. B) is used to understate the rate of inflation. C) is a useful tool for determining which fence to purchase. D) uses neighboring years' data to calculate changes in nominal GDP.
Distinguish between implicit and explicit costs and give examples of each. In addition, explain how explicit and implicit costs affect the distinction between economic profit and accounting profit
What explains the distinction between the two measures of profit?
The estimated demand for a good is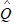 = 4800 - 16P - 0.65M - 1.5PRwhere Q is the quantity demanded of the good, P is the price of the good, M is income, and PR is the price of related good R. This good and good R are
= 4800 - 16P - 0.65M - 1.5PRwhere Q is the quantity demanded of the good, P is the price of the good, M is income, and PR is the price of related good R. This good and good R are
A. complements since the coefficient on PR is negative. B. substitutes since the coefficient on M is negative. C. complements since the coefficient on M is negative. D. substitutes since the coefficient on PR is negative. E. none of the above