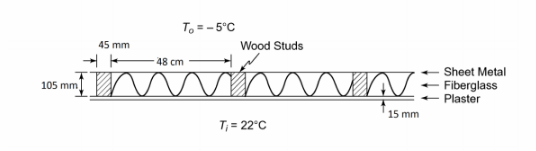
The ceiling of a tract house is constructed of wooden studs with fiberglass insulation between them. On the interior of the ceiling is plaster and on the exterior is a thin layer of sheet metal. A cross section of the ceiling with dimensions is shown below. (a) The R-factor describes the thermal resistance of insulation and is defined by: R-factor = L/keff = ?T/(q/A) Calculate the R-factor for this type of ceiling and compare the value of this R-factor with that for a similar thickness of fiberglass. Why are the two different? (b) Estimate the rate of heat transfer per square meter through the ceiling if the interior temperature is 22°C and the exterior temperature is –5°C.
GIVEN
FIND

ASSUMPTIONS
- Steady state heat transfer
- One dimensional conduction through the ceiling
- Thermal resistance of the sheet metal is negligible
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
Pine or fir wood studs (kw) = 0.15 W/(m K) at 20°C
Fiberglass (kfg) = 0.035 W/(m K) at 20°C
Plaster (kp) = 0.814 W/(m K) at 20°C
The thermal circuit for the ceiling with studs is shown below
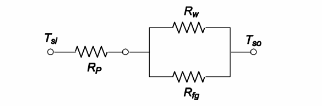
where Rp = thermal resistance of the plaster
Rw = thermal resistance of the wood
Rfg = thermal resistance of the fiberglass
Each of these resistances can be evaluated
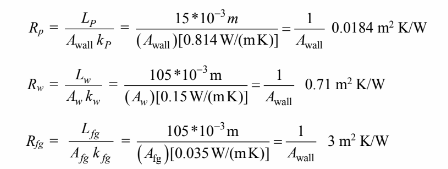
To convert these all to a wall area basis the fraction of the total wall area taken by the wood studs and
the fiberglass must be calculated
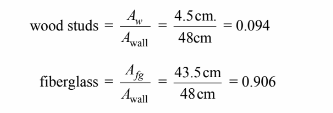
Therefore the resistances of the studs and the fiberglass based on the wall area are
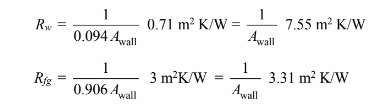
The R-Factor of the wall is related to the total thermal resistance of the wall by
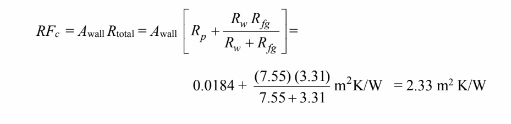
For 120 mm. of fiberglass alone, the R-factor is
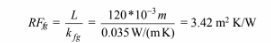
The R-factor of the ceiling is only 68% that of the same thickness of fiberglass. This is mainly due to
the fact that the wood studs act as a ‘thermal short’ conducting heat through the ceiling more quickly
than the surrounding fiberglass.
(b) The rate of heat transfer through the ceiling is
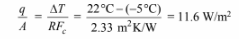
You might also like to view...
Which of the following statements is true?
A. Even though X-rays have higher energy, they move with the same speed as that of visible light. B. X-rays have higher energy, but still they move slower than visible light. C. X-rays have higher energy, hence they move faster than visible light. D. None of these choices are correct.
A person approaches a plane mirror at a speed of 3 m/s. How fast does he approach his image?
A) 3 m/s B) 4 m/s C) 5 m/s D) 6 m/s E) 7 m/s
A 1.30-m long gas column that is open at one end and closed at the other end has a fundamental resonant frequency 80.0 Hz. What is the speed of sound in this gas?
A) 104 m/s B) 61.5 m/s C) 26.0 m/s D) 246 m/s E) 416 m/s
Orbital Angular Momentum: What is the minimum angle between the z-axis (or any other axis you choose) and the orbital angular momentum of an electron in the n = 4 state?
A. 30.0° B. 41.4° C. 60.0° D. 45.0°