Refer to the below table. In the first game:
Answer the question based on the following payoff matrices for a repeated game involving two firms that are considering introducing new products to the market. The numbers indicate the profit from following either a strategy to introduce a new product or a strategy to not introduce a new product.
First game:
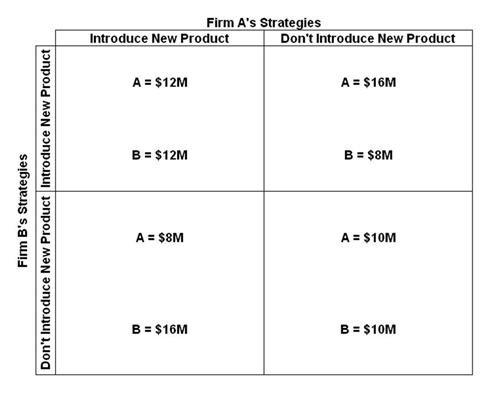
A. Introducing a new product is the dominant strategy for both firms
B. Not introducing a new product is the dominant strategy for both firms
C. Introducing a new product is the dominant strategy for firm A while not introducing a new product is the dominant strategy for firm B
D. Not introducing a new product is the dominant strategy for firm A while introducing a new product is the dominant strategy for firm B
A. Introducing a new product is the dominant strategy for both firms
You might also like to view...
For a firm in monopolistic competition, define efficient scale and excess capacity. Briefly explain each
What will be an ideal response?
In long-run macroeconomic equilibrium
A) real GDP equals potential GDP. B) the price level is fixed and aggregate demand determines real GDP. C) real GDP and the price level are determined by short-run aggregate supply and aggregate demand and long-run aggregate supply is irrelevant. D) real GDP is less than potential GDP.
Which of the following ideas are NOT demonstrated by the PPF?
a. Efficiency b. Scarcity c. Opportunity cost d. Diminishing returns to scale
A market equilibrium might not maximize total economic surplus because:
A. in a market equilibrium individuals do not exploit all opportunities for individual gain. B. sometimes goods entail costs and benefits that do not fall on buyers and sellers. C. in a market equilibrium individuals do not act rationally. D. efficiency is not an important social goal.