The examination position pictured here is the ________ position.
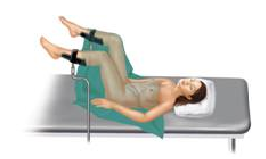
lithotomy
The patient is shown in the lithotomy position.
You might also like to view...
You are by the side of an unresponsive 6-month-old with a history of congenital heart disease. The patient's airway is patent, but he is not breathing. A heart rate of 24 beats per minute is noted. At this time, it is essential that you:
A) apply the AED with pediatric pads. B) start cardiopulmonary resuscitation. C) start positive pressure ventilation with high-concentration oxygen. D) place the patient on the stretcher for immediate and emergent transport.
An elderly patient has fallen down a flight of stairs and is complaining of neck and back pain and weakness to both legs. Your primary assessment reveals no life threats to the airway, breathing, or circulation. Manual in-line spinal stabilization is being maintained. Which of the following actions should you take next?
a. apply high-flow oxygen and move the patient to a stretcher for transport. b. complete a secondary assessment looking for injuries. c. place an oral airway and begin assisting ventilation. d. place a cervical collar on the patient and immobilize him to a long spine board.
If a patient is released from a WC claim with a permanent disability settlement and the provider has unpaid fees, the provider is likely to:
a. place a lien on the settlement. b. write off the unpaid fees. c. bill the patient. d. stop treating the patient.
Which of the following occurs during the expulsion phase of the birthing process?
A. The actual birth of the baby B. The third and final stage of childbirth begins C. The breaking of the amniotic sac D. The cervix dilates between 4 and 8 cm