A charged particle (mass = 4.0 ?g, charge = 5.0 ?C) moves in a region where the only force on it is magnetic. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the particle at a point where the speed of the particle is 5.0 km/s, the magnitude of the magnetic field is 8.0 mT, and the angle between the direction of the magnetic field and the velocity of the particle is 60°?
A. 39 km/s2
B. 43 km/s2
C. 48 km/s2
D. 52 km/s2
E. 25 km/s2
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The observation of the moons of Jupiter by Galileo Galilei suggested that:
A) Earth could not move as its moon would be left behind. B) the Solar System was actually geocentric. C) Earth could move and keep its moon. D) the only center of motion was Earth.
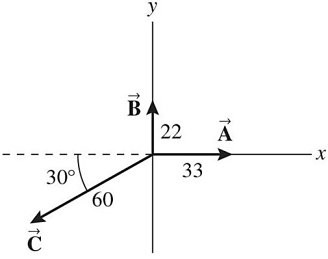
Addition by 1. Components: The figure shows three vectors, src="https://sciemce.com/media/4/ppg__cp1pbb0313192044__f15g1q36g6.jpg" style="vertical-align: -5.0px;" />.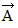 ,
, 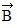 , and
, and 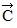 , along with their magnitudes. Determine the magnitude and direction of the vector given by
, along with their magnitudes. Determine the magnitude and direction of the vector given by  +
+  -
- 
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
Why does the Main Sequence part of a star's life end?
A: Much of the mass of the star has evaporated B: The Hydrogen in the core is exhausted C: The Helium in the core is exhausted D: The temperature drops so that nuclear reactions are no longer possible E: The gravitational force is no longer large enough to balance the pressure
A steel pipe (E 5 190 GPa, ? 5 14 3 1026/°C, d2 5 82 mm, and d1 5 70 mm) of length L 5 4.25 m hangs from a rigid surface and is subjected to a temperature increase ¢T 5 50 °C. The column is fixed at the top and has a small gap at the bottom. To avoid buckling, the mini-mum clearance at the bottom should be approximately:
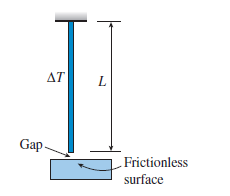
(A) 2.55 mm
(B) 3.24 mm
(C) 4.17 mm
(D) 5.23 mm