Assume that the expectation of declining housing prices cause households to reduce their demand for new houses and the financing that accompanies it. If the nation has low mobility international capital markets and a flexible exchange rate system, what happens to the quantity of real loanable funds per time period and the nominal value of the domestic currency in the context of the
Three-Sector-Model?
a. The GDP Price Index rises, and nominal value of the domestic currency falls.
b. The GDP Price Index falls, and nominal value of the domestic currency rises.
c. The GDP Price Index rises, and nominal value of the domestic currency remains the same.
d. The GDP Price Index falls, and nominal value of the domestic currency falls.
e. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.
.D
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as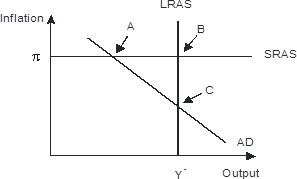
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward C. Aggregate demand shifting rightward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
The term "free riders" refers to people who:
A) selflessly pay for others' consumption of goods and services. B) make economic decisions randomly and are not rational. C) haggle over the prices of the goods and services that they buy. D) don't contribute but still benefit from others' actions.
The slope of the consumption function is called the:
a. autonomous consumption rate. b. marginal consumption rate. c. average propensity to consume. d. marginal propensity to consume.
When we examine historical data on income inequality in the U.S., we see that the distribution of income gradually became
a. more equal between 1935 and 2011. b. more equal between 1935 and 1973, but that trend reversed itself between 1973 and 2011. c. more unequal between 1935 and 1973, but that trend reversed itself between 1973 and 2011. d. more unequal between 1935 and 2011.