We don't need to draw separate curves for demand, average revenue, and marginal revenue curves for a perfectly competitive firm. Why?
Under perfect competition the firm's demand curve, average revenue curve, and marginal revenue curve are all the same. A firm's demand curve is also its average revenue curve if it sells its product at the same price to each and every customer, because the average revenue a firm gets from selling a commodity is equal to the price of the commodity. In perfect competition, the price does not depend on how much the firm sells. Then each additional unit sold brings in an amount of additional revenue (the marginal revenue) exactly equal to the market price which means marginal revenue always equals price under perfect competition.
You might also like to view...
In the long run, an increase in government spending, other things equal, generates
A) a higher real GDP in the long run. B) a lower real GDP in the short run. C) a higher price level. D) both a higher real GDP and a lower price level.
The entry of new firms into an industry will very likely
A. shift the industry supply curve to the right. B. cause the market price to fall. C. reduce the profits of existing firms in the industry. D. All of the responses are correct.
Ceteris paribus, if the market supply of a product decreases, then equilibrium quantity will (be) ____ and equilibrium price will (be) ____
a. increase; increase b. decrease; increase c. decrease; indeterminate d. increase; decrease
A radio manufacturer is experiencing theft problems at its warehouse and has decided to hire security guards to reduce the thefts. The firm wants to minimize the net cost of warehouse thefts. 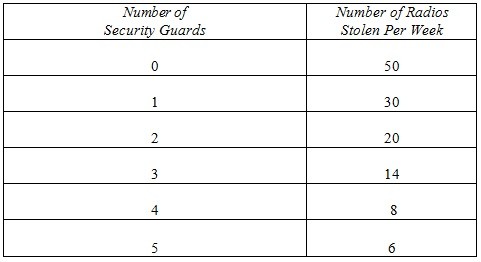 Given the above info, if each security guard is paid $200 a week and the cost of a stolen radio is $25, how many security guards should the firm hire?
Given the above info, if each security guard is paid $200 a week and the cost of a stolen radio is $25, how many security guards should the firm hire?
A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 E. 5