What is the function of polar bodies?
A. They provide nourishment for the developing embryo.
B. They prevent more than one sperm from entering the egg.
C. They produce hormones that allow ova to develop properly.
D. They provide fructose to the semen for sperm motility.
E. None of these are functions of polar bodies.
E
You might also like to view...
The "9 + 2" pattern of the axoneme is nine ________ of microtubules and two additional microtubules in the center called the ________.
A) outer doublets; central pair B) basal bodies; inner two C) central tubules; double pair D) circular structures; middle two E) triplet groups; basal bodies
Which of the following molecules is most directly involved in the transfer of energy from food to the proton pumps depicted in this figure?
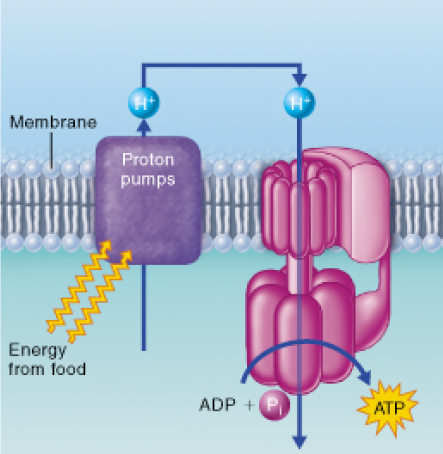
a. ATP
b. NADH
c. oxygen
d. ADP
What is the significance of the industrial practice of waiting for cultures to enter the stationary phase of growth before harvest?
A) The cells are at peak metabolic activity. B) Secondary metabolites are often the desired product, and are only produced in stationary phase. C) The desired primary metabolites are produced in stationary phase. D) Potential toxins from log phase growth have been depleted. E) An optimal combination of primary and secondary metabolites is being produced.
In a capsule stain, capsules can be seen as ___________ surrounding the cells.
A. Purple cells walls B. Pink cell walls C. Clear halos D. A dark background