Jeremy purchases a bond that pays $600 in interest. If Jeremy paid $9,000 for the bond, what is the interest rate? If Jeremy paid $10,000 for the bond, what is the interest rate? How did a rise in the price of the bond affect the interest rate?
What will be an ideal response?
When Jeremy paid $9,000 for the bond, the interest rate is ($600 ÷ $9,000 ) × 100 = 6.67 percent. When Jeremy paid $10,000 for the bond, the interest rate is ($600 ÷ $10,000 ) × 100 = 6.00 percent. The rise in the price of the bond brought about a fall in its interest rate.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is an intermediate good?
A. Tomatoes sold in the grocery store that you use to make salsa. B. Tomatoes grown in your garden that you use to make salsa. C. Tomatoes sold to a factory and used in the production of spaghetti sauce. D. Tomatoes you buy at a local farmer's stand that you use to make salsa.
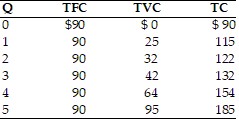 Refer to the above table. When output rises from 4 units to 5 units, marginal costs are
Refer to the above table. When output rises from 4 units to 5 units, marginal costs are
A. $22. B. $10. C. $31. D. $19.
On average, the inventory/sales ratio has been ________ over time.
A. increasing B. unchanged C. declining D. very volatile
The concept of opportunity cost
A. can be applied to the analysis of any decision-making process. B. applies to consumers but not to firms. C. refers only to actual payments and incomes. D. is relevant only to economics.