How do the size and chemical composition of a planet determine its internal temperature?
What will be an ideal response?
Size is the most important factor in determining how rapidly a planet loses its internal heat. The larger a planet is, the deeper is the "insulation" that surrounds the core and keeps in the heat. The chemical composition of a planet determines the amount of radioactive elements present. Currently the terrestrial planets' primary source of heat is radioactivity.
You might also like to view...
Temperature Scales: Oxygen condenses into a liquid at approximately 90 K. What temperature, in degrees Fahrenheit, does this correspond to?
A. -193°F B. -217°F C. -265°F D. -297°F
Magnetic Field of a Long Wire: A long straight wire carrying a 4-A current is placed along the x-axis as shown in the figure. What is the direction of the magnetic field at a point P due to this wire?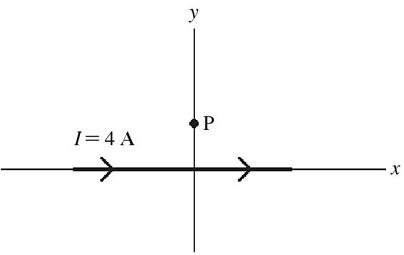
A. into the plane of the page B. out of the plane of the page C. along the -x-axis D. along the +x-axis E. along the +y-axis
A car has a mass of 1000 kg and accelerates at 2 m/s2. What net force is exerted on the car?
A) 500 N B) 1000 N C) 1500 N D) 2000 N E) none of these
Which of the following describes volcanism?
A) the excavation of bowl-shaped depressions by asteroids or comets striking a planet's surface B) the eruption of molten rock from a planet's interior to its surface C) the disruption of a planet's surface by internal stresses D) the wearing down or building up of geological features by wind, water, ice, and other phenomena of planetary weather