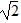An object of mass m is attached to a horizontal spring, stretched to a displacement A from equilibrium and released, undergoing harmonic oscillations on a frictionless surface with period T0. The experiment is then repeated with a mass of 4m. Choose the new period of oscillation
1. 2T0
2. T0
3. T0/2
4. T0/4
1
You might also like to view...
If stars rotate with periods of tens of days, why does a neutron star rotate several to thousands of times a second?
A. When a neutron star collapses, its rotation rate speeds up because of conservation of angular momentum. B. The collapsing neutron star becomes hot and the fast rotation is the result of thermal energy. C. When a neutron star collapses, its rotation is kicked up by the ejected material from the supernova. D. When a neutron star collapses, the intensified magnetic field causes it to rotate much more quickly.
Energy Levels: A highly ionized atom with Z = 5 has only one electron left around it, in its ground state. How much more energy is required to finish the job and have a bare nucleus?
A. 340.0 eV B. 68.0 eV C. 10.9 eV D. 13.1 eV
How do x-ray measurements help us measure the amount of dark matter in galaxy clusters?
A) The gravity of dark matter causes intracluster gas to be heated to very high temperatures, and the higher the temperature, the stronger the x-ray emission we will detect from the gas. B) Dark matter absorbs x-rays, so we can map the dark matter distribution by looking for absorption lines in x-ray spectra. C) Collisions between dark matter particles emit x-rays, allowing us to map dark matter with x-ray images.
Parallel Wires: When two long parallel wires carry unequal currents, the magnitude of the magnetic force that one wire exerts on the other is F. If the current in both wires is now doubled, what is the magnitude of the new magnetic force on each wire?
A. 16F
B. 8F
C. 4F
D. 2F
E. F