A beam of light that is parallel to the principal axis is incident on a concave mirror. What happens to the reflected beam of light?
A)
It also is parallel to the principal axis.
B)
It is perpendicular to the principal axis.
C)
It passes through the center of curvature of the mirror.
D)
It passes through the focal point of the mirror.
E)
It passes between the focal point and the center of curvature of the mirror.
D
You might also like to view...
A grand unified theory (GUT) refers to a type of theory intended to unify
A) the strong force with the electromagnetic and weak forces. B) gravity with the strong and weak forces. C) the electromagnetic and weak forces. D) all four forces together.
Which of the following is not used as a distance indicator for galaxies?
a. Large globular clusters b. Herbig-Haro objects c. H II regions d. Cepheid variable stars e. Supernovae
For the circuit shown, what is the rate of change of the current in the inductor when the current in the battery is 0.50 A?
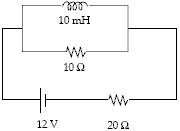
a.
600 A/s
b.
400 A/s
c.
200 A/s
d.
800 A/s
e.
500 A/s
The largest known black holes:
A) create the dark nebulae in the plane of the Milky Way. B) can be no more than 1.4 solar masses, according to Chandrasekhar. C) lie in the cores of the most massive galaxies. D) can be no bigger than a small city, just like neutron stars. E) can be no bigger than the Earth, like white dwarfs.