Suppose a manager views both quantity and profit as "goods." Such a manager will then have an indifference curve that: 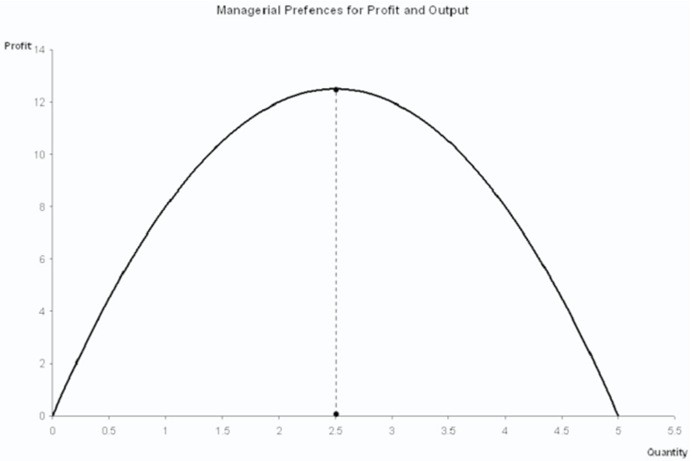
A. is tangent to the profit curve somewhere between quantities of 0 and 2.5.
B. intersects the profit curve at a quantity exactly equal to 2.5.
C. is tangent to the profit curve somewhere between quantities of 2.5 and 5.
D. intersects the profit curve at a quantity exactly equal to 5.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
The leading example of sampling schemes in econometrics that do not result in independent observations is
A) cross-sectional data. B) experimental data. C) the Current Population Survey. D) when the data are sampled over time for the same entity.
Risky transactions are those in which:
A. complete information is not available. B. there is an balance of information between buyer and seller. C. one party to a transaction uses the other party's lack of information to their advantage. D. one party withholds information from the other party and uses that to his advantage.
The main function of the Federal Reserve System is to:
A. supervise the operation of member banks. B. control the money supply. C. serve as the fiscal agent for the federal government. D. clear checks from member banks.
Owen and Simon both like playing with balls and cars. Suppose B represents the number of balls, and C represents the number of cars. If Owen's utility function can be given by U(B, C) = 10B + 5C, and Simon's utility function can be given by U(B, C) = 6B + 6C, which of the following trades would benefit Simon but not Owen?
A. Owen gives Simon 3 cars in exchange for 2 balls B. Owen gives Simon 2 cars in exchange for 3 balls C. Owen gives Simon 3 balls in exchange for 2 cars D. Owen gives Simon 2 balls in exchange for 3 cars