If excess charge is put on a spherical nonconductor,
A) it remains where it was placed
B) it spreads a little from where it was placed but not over the whole sphere
C) it spreads uniformly over the surface of the sphere if the sphere is small
D) it spreads uniformly throughout the volume of the conductor
E) it spreads uniformly over the surface of the sphere
A) it remains where it was placed
You might also like to view...
Observations of the cosmic background radiation from the COBE satellite revealed tiny variations in its temperature by about 1 part in 100,000
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The most important reason an object is observed to be shorter in a frame where it is moving than in a frame where it is at rest is that
A. The force of motion strongly compresses an object that is moving at relativistic speeds. B. “Simultaneity” is not a frame-independent concept. C. The measuring sticks used by the moving observer are Lorentz-contracted. D. The clocks used by the moving observer run slower.
The wavelength of a wave multiplied by the frequency of the wave is the wave's
a. speed b. frequency c. wavelength d. amplitude e. loudness
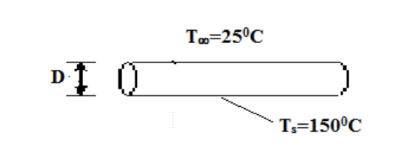
A long, heated, cylindrical steel rod is removed from a heat treatment furnace and has to be cooled to complete the process. If the surface temperature of the rod is at 150°C and the cooling fluid temperature is maintained at 25°C, what is the minimum diameter of the rod to produce turbulent natural convection heat transfer if it is held in a horizontal position in (a) air and (b) water? Also, determine the initial heat transfer rate by natural convection from a 10-cm diameter rod in each of the two fluids.
GIVEN
• Long heated cylindrical steel rod, cooled by natural convection.
• Surface temperature of rod (Ts=1500C
• Fluid temperature (T?) = 250C
FIND
(a) Minimum diameter of rod to produce turbulent natural convection in (i) Air (ii) water
(b) Initial heat transfer rate by natural convection from 10 cm diameter rod in each fluids.
ASSUMPTIONS
• Radiation is negligible
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for dry air at the mean temperature of 87.5°C
Thermal expansion coefficient (?) = 0.00277 1/K
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0298 W/(m K)
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 22.55 × 10–6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71
for water at the mean temperature of 87.5°C
Thermal expansion coefficient (?) = 0.000678 1/K
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.6765 W/(m K)
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 0.33 × 10–6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 67.8