Solve the problem.Let Q(x) = bo + b1(x - a) + b2(x - a)2 be a quadratic approximation to f(x) at x = a with the properties:i. Q(a) = f(a)ii. Q '(a) = f '(a)iii. Q "(a) = f "(a)(a) Find the quadratic approximation to f(x) = 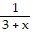 at x = 0.(b) Do you expect the quadratic approximation to be more or less accurate than the linearization? Give reasons for your answer.
at x = 0.(b) Do you expect the quadratic approximation to be more or less accurate than the linearization? Give reasons for your answer.
What will be an ideal response?
(a) Q(x) = 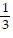 -
- 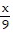 +
+ 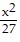
(b) I expect the quadratic approximation to be more accurate than the linearization. The linearization accounts for how the value of f(x) is changing at the point x = a, but the quadratic approximation also accounts for the change in this change by incorporating the second derivative into the approximation.
You might also like to view...
An x-ray of a patient's leg is done with a current setting of 30mA for a time of 1s. If none of the distances is changed and the current is increased to 60mA, what should the exposure time be?
A. 2s B. 4s C. 0.5s D. 0.25s
Solve. Write a mixed numeral for the answer.Daniel is 70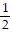 in. tall and his brother Tyler is 67
in. tall and his brother Tyler is 67 in. tall. How much taller is Daniel?
in. tall. How much taller is Daniel?
A. 2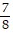 in.
in.
B. 3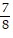 in.
in.
C. 2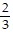 in.
in.
D. 3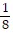 in.
in.
Use substitution to determine whether the given ordered pair is a solution of the given equation.(4, 3); x2 + y2 = 25
A. Yes B. No
Find the slope and y-intercept of the line.-x + 2y = 8
A. slope = 2; y-intercept = -8
B. slope = -1; y-intercept = 8
C. slope = - 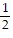 ; y-intercept = 4
; y-intercept = 4
D. slope = 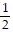 ; y-intercept = 4
; y-intercept = 4