A rod system with a uniform linear density of l = 4.40 kg/m has the shape shown in the figure, with rod 1 the vertical rod and rod 2 the horizontal rod. Rod 1 has length L1 = 8.00 m, and rod 2 has length L2 = 7.50 m. Neglect the diameter of the rods
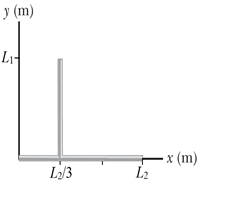
?
What is the center of mass of each rod?
a.
rod 1: (35.20 m, 0), rod 2: (0, 11.73 m)
b.
rod 1: (17.60 m, 0), rod 2: (0, 16.50 m)
c.
rod 1: (2.50, 4.00), rod 2: (3.75 m, 0 m)
d.
rod 1: (10.20 m, 0), rod 2: (0, 9.70 m)
?
c
You might also like to view...
Light reflects off the surface of Lake Superior. What phase shift does it undergo?
A) 0° B) 90° C) 180° D) 270° E) It does not undergo any phase shift.
How will the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) and the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) observe gravitational waves?
a. They will detect vibrations in very long solid metal cylinders. b. They will use laser light to detect tiny changes in the distance between mirrors placed far away from each other. c. They will measure the force on precision masses at the ends of long tunnels from a large moving mass in the central building. d. They will measure the changes in the attraction between two masses as one rotates past the other suspended from a thin metal wire. e. They will measure changes in frequency of two masses swinging past each other.
What is the gravitational force between two 7.00-kg balls, when they are 35.0 cm apart? G = 6.67 x 10-11 N•m2/kg2
What will be an ideal response?
The distance to a hypothetical galaxy is estimated at about 7 × 10^6 light years. A light year is the distance traveled by light in one year; if the speed of light is 3 × 10^8 m/s, about how far is it from our galaxy to this hypothetical galaxy? (1 year = 3.15 × 10^7 s)
a. 7E+21 m b. 1E+9 m c. 7E+22 m d. 7E+5 m