The model: G(z) = 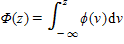 , where
, where  (z) = (2
(z) = (2
/>)-1/2exp(-z2/2) represents a:
A. Tobit model.
B. logit model.
C. probit model.
D. linear probability model.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is true when profit-maximizing firms in a competitive market are allowed to freely emit negative externalities on society?
a. Consumers are paying a market equilibrium price that reflects the full social marginal cost of production. b. Consumers are paying a market equilibrium price that reflects only the external marginal cost of production. c. Consumers are paying a market equilibrium price that is less than the socially efficient price, and consuming more than the socially efficient quantity. This means society is implicitly subsidizing producers by allowing them to pollute. d. None of the above is correct.
What are the prerequisites for money creation?
Which of the following statements is true?
A) In the monetarist transmission mechanism, changes in the money market directly affect aggregate demand. B) In the monetarist transmission mechanism, there is no need for the money market to affect the loanable funds market or investment before aggregate demand is affected. C) In the monetarist transmission mechanism, if individuals are faced with an excess supply of money, they spend that money on a wide variety of goods---not just bonds or other assets, as is the case in the Keynesian transmission mechanism. D) a and b E) a, b and c
Suppose that labor is mobile between countries A and B. If the relative demand for goods rises in country A, then labor can flow from ______________. It may be possible in this situation for countries A and B to __________________ which would help to___________________
A) country A to country B; fix the exchange rate between the two countries (or have a common currency); eliminate the risks associated with having a flexible exchange rate. B) country B to country A; impose trade restrictions upon one another; increase employment in country A C) country B to country A; fix the exchange rate between the two countries (or have a common currency); eliminate the risks associated with having a flexible exchange rate D) country A to country B; adopt flexible exchange rates; reduce the risk of exchange rate fluctuations