A counterflow regenerator is used in a gas turbine power plant to preheat the air before it enters the combustor. The air leaves the compressor at a temperature of 350°C. Exhaust gas leaves the turbine at 700°C. The mass flow rates of air and gas are 5 kg/s. Take the cp of air and gas to be equal to 1.05 kJ/(kg K). Determine the required heat transfer area as a function of the regenerator effectiveness, if the overall heat transfer coefficient is 75 W/(m2 K).
GIVEN
• Counterflow air-to-gas heat exchanger
• Entering temperatures
? Ta,in = 350°C
? Tg,in = 700°C
• Mass flow rates: m a= 5 kg/s
• Specific heats: cpa = cpg = 1.05 kJ/(kg K) = 1050 J/(kg K)
• Overall heat transfer coefficient (U) = 75 W/(m2 K)
FIND
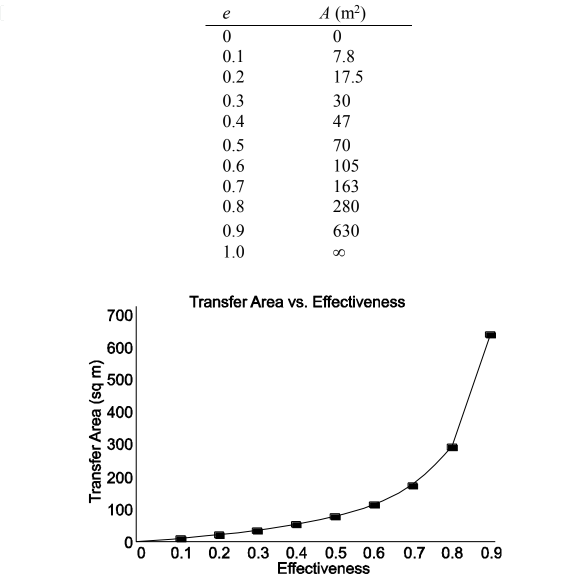
• The heat transfer area (A) as a function of the effectiveness (e)
SKETCH
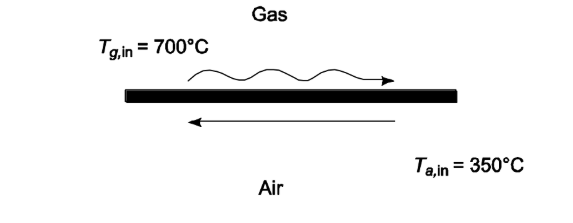
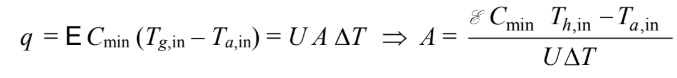
Since ma cpa = mg cpg, the temperature difference between the gas and air remain constant and ?T = Tg,in Ta,out . The heat capacity rates are equal, therefore reduces to
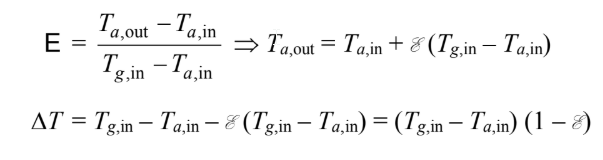
Substituting this into the expression for area
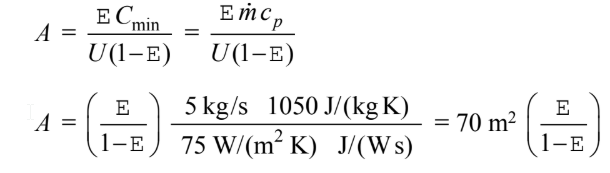
This is tabulated and plotted below
COMMENTS
This problem can also be solved by calculating the number of transfer units for a given area then reading the effectiveness off
You might also like to view...
In a collision between two objects having unequal masses, how does magnitude of the impulse imparted to the lighter object by the heavier one compare with the magnitude of the impulse imparted to the heavier object by the lighter one?
A) The lighter object receives a larger impulse. B) The heavier object receives a larger impulse. C) Both objects receive the same impulse. D) The answer depends on the ratio of the masses. E) The answer depends on the ratio of the speeds.
A metal rod of length L in a region of space where a constant magnetic field points into the page rotates clockwise about an axis through its center at constant angular velocity ?. While it rotates, the point(s) at lowest potential is(are)
A. A. B. B. C. C. D. D. E. A and E.
A mass is oscillating on a spring with a period of 4.60 s. At t = 0 s the mass has zero speed and is at x = 8.30 cm. What is the value of t the first time after t = 0 s that the mass is at x = 4.15 cm?
A) 0.575 s B) 0.767 s C) 1.15 s D) 1.30 s E) 1.53 s
The deBroglie wavelength for a particle indicates its
A. position B. momentum C. mass D. physical extent in space