To find the market demand curve for in-line skates, we must
A) add the quantities demanded at every price and every income by every buyer of in-line skates.
B) add the quantities demanded at prices that all buyers can afford to pay.
C) take account of the skate buying plans of all actual and potential buyers in all possible situations.
D) sum horizontally the individual demand curves of all the buyers.
E) None of the above answers is correct because we need also to take account of the supply of in-line skates.
D
You might also like to view...
The largest component of GDP is:
a. personal consumption expenditures. b. government spending. c. durable goods. d. net exports. e. gross private domestic investment.
Which of the following statements about straight-line demand curves is true?
a. The price elasticity of demand becomes larger in absolute value as price falls. b. The price elasticity of demand becomes smaller in absolute value as price falls. c. The price elasticity of demand is constant along the curve. d. The price elasticity of demand and the slope of the demand curve are the same. e. Demand is price elastic everywhere along the curve.
If by international treaty the ratio of the price of services to the price of goods was held at 1.5, then
Suppose Canada can produce either 120 units of goods, 80 units of services, or any linear combination thereof. Mexico can produce 90 units of goods, 50 units of services, or any linear combination thereof. a) neither country would benefit from trade b) both countries will benefit from trade c) only Canada would benefit from trade; Mexico would lose d) only Mexico would benefit from trade; Canada would lose e) Mexico would benefit from trade; Canada would neither gain nor lose
In Figure 23.1, for a good with no externality, which area represents the net benefit to society of this market? 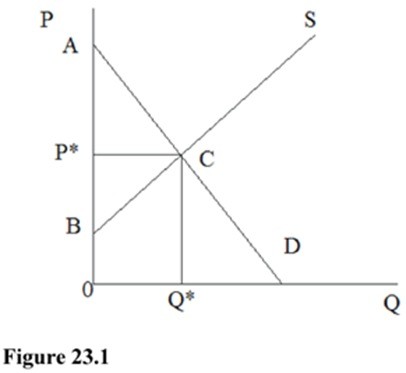
A. BP*C B. ABC C. 0ACQ* D. 0P*CQ*