Compare olfactory receptors with receptors for the other special senses
A) Olfactory receptors are at the surface of the olfactory epithelium and can generate a fast action potential, whereas receptors for the other special senses are deep and slower to generate an action potential.
B) Olfactory receptors are chemoreceptors and respond to dissolved chemicals, whereas the receptors for the other special senses are mechanoreceptors.
C) Olfactory receptors have short axons because of their close proximity to the olfactory bulb, whereas the receptors for the other special senses have long axons because they are further away from the CNS.
D) Olfactory receptors do not require the CNS for processing the signal, whereas the receptors for the other special senses require processing by the CNS.
E) Olfactory receptors are the dendrites of specialized excitable olfactory neurons, whereas the receptors for the other special senses are receptor cells with inexcitable membranes and form synapses with the processes of sensory neurons.
Answer: E
You might also like to view...
Which organelle contains the nucleolus?
A. The mitochondrion B. The Golgi apparatus C. The nucleus D. The endoplasmic reticulum
How are the neuron cell body are called when they are all clustered together in masses in the PNS?
A. Axon Terminal B. Ganglia C. Plexus D. Ligaments
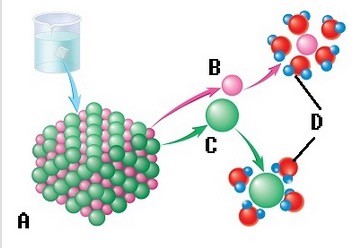 The sodium chloride molecule breaks apart in water. What does "A" represent?
The sodium chloride molecule breaks apart in water. What does "A" represent?
A. Salt crystal B. Sodium ion C. Water molecule D. Dissociation E. Chloride ion
What conditions favor the proliferation of intestinal microbiota in the large intestine?
A. The anaerobic environment of the large intestine B. The undigested sugars and amino acids that regularly enter the large intestine C. The use of antibiotics D. The presence of Vitamin K and Vitamin B12