The most powerful agent of erosion is
A) stream flow.
B) glacial action.
C) action from waves and ocean currents.
D) wind.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The interior of a greenhouse emits long-wavelength radiation due to its
A) green color. B) plant cell structure. C) transparency. D) relatively low temperature.
The circuit below contains 5 identical light bulbs. The emf is 110 V. Which light bulb(s) is(are) brightest?

a.
A: The one closest to the positive terminal of the battery.
b.
A and C: The bulbs closest to the positive terminal of the battery.
c.
A and B: Because they are closest to the terminals of the battery.
d.
C and D: Because they receive current from A and B and from E.
e.
E: Because the potential difference across E is that of the battery.
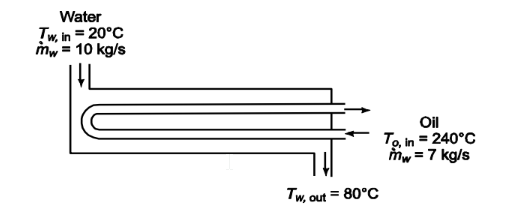
Oil c p2.1 kJ/(kg K) is used to heat water in a shell and tube heat exchanger with a single shell and two tube passes. The overall heat transfer coefficient is 525 W/(m2 K). The mass flow rates are 7 kg/s for the oil and 10 kg/s for the water. The oil and water enter the heat exchanger at 240°C and 20°C, respectively. The heat exchanger is to be designed so that the water leaves the heat exchanger with a minimum temperature of 80°C. Calculate the heat transfer surface area required to achieve this temperature.
GIVEN
• Oil heats water in a heat exchanger with one shell pass and two tube passes
• Oil specific heat (cpo) = 2.1 kJ/(kg K) = 2100 J/(kg K)
• Overall heat transfer coefficient (U) = 525 W/(m2 K)
• Oil mass flow rate m o= 7 kg/s
• Water mass flow rate m w= 10 kg/s
• Inlet temperatures: Oil (To,in) = 240° Water (Tw,in) = 20°C
• Minimum water outlet temperature (Tw,out) = 80°C
FIND
• The heat transfer area (A) required
ASSUMPTIONS
• Oil is in the tubes
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the specific heat of water at the average temperature of 50°C (cpw)= 4178 J/(kg K)
The first attempt to map the Galaxy via star counts was done by
A) William Herschel in the late eighteenth century. B) Edwin Hubble with the new 100" Mt. Wilson telescope in the 1930s. C) Harlow Shapley with the RR Lyrae variables in 1920. D) Edward Barnard with long exposure photos about 1900. E) Galileo in 1612.