Marginal social costs are the sum of marginal private costs and incidental costs
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
True
You might also like to view...
Answer the next question using the figure below.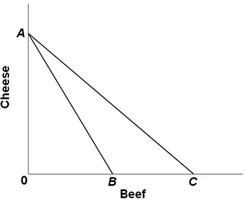 In the diagram, line AB is the U.S. production possibilities curve and line AC shows the consumption possibilities for the U.S. after it has decided to engage in international trade. We can conclude that the United States
In the diagram, line AB is the U.S. production possibilities curve and line AC shows the consumption possibilities for the U.S. after it has decided to engage in international trade. We can conclude that the United States
A. has decided to trade beef for cheese. B. has chosen to specialize in the production of cheese. C. is relatively more efficient than its trading partners in producing both cheese and beef. D. has chosen to specialize in the production of beef.
Refer to the figure above. The equilibrium exchange rate in this case is:
A) 40 rupees per dollar. B) 80 rupees per dollar. C) 130 rupees per dollar. D) 20 rupees per dollar.
The experience of the former Soviet bloc countries illustrates that high rates of investment may fail to promote rapid economic growth when a country
a. uses central government planning rather than capital markets to allocate investment funds. b. has a strong education system. c. has secure property rights. d. has a tax system that encourages savings.
As Europe explored monetary union, evidence to date suggests that increased variability in exchange rates
A) reduces foreign trade and investment. B) increases foreign trade and investment. C) does not seem to have an impact on foreign trade and investment. D) hurts foreign investment but not trade.