Vegetations are associated with which of the following disease processes?
A) septicemia
B) endocarditis
C) tularemia
D) plague
E) toxoplasmosis
B
You might also like to view...
The following graph shows the relationship between extinction and habitat area. Which statements help explain the trend shown on the graph? Check all that apply.
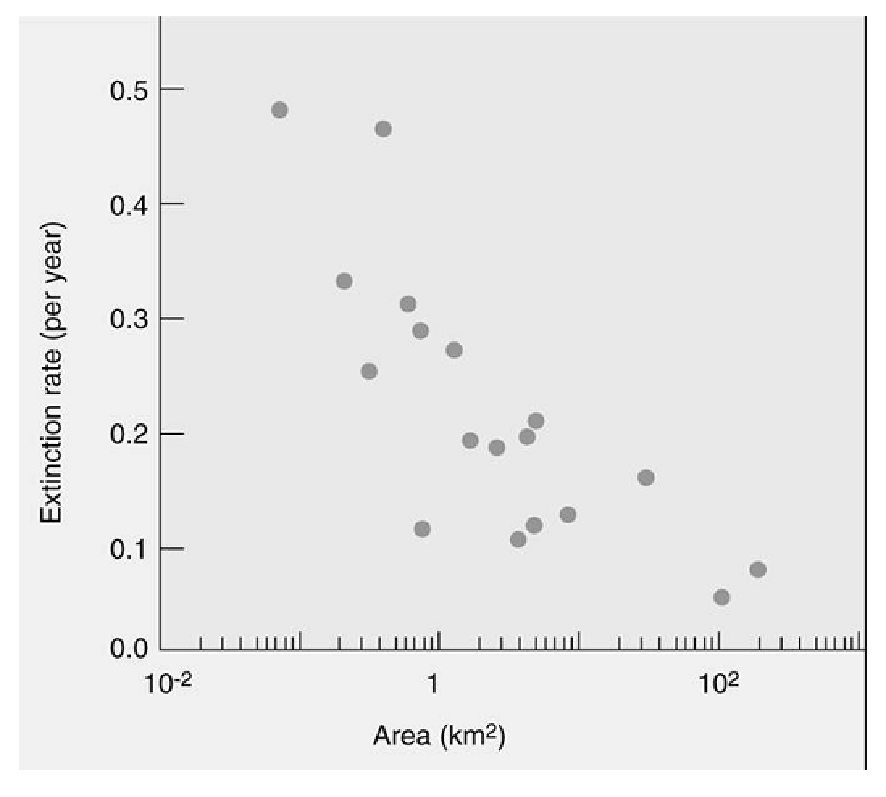
_____ Larger patches are more likely to be encountered by new immigrants.
_____ Larger patches are likely to have a more uniform habitat.
_____ Larger patch size reduces genetic drift.
_____ Larger patches are more geographically isolated than smaller patches.
_____ Species richness is higher on larger patches.
Additional:
Clarify Question
· What is the key concept addressed by the question?
Gather Content
· What do you already know about habitat area and extinction?
Choose Answer
· Given what you now know, what information and/or problem solving approach is most likely to produce the correct answer?
Reflect on Process
· Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
In photosynthesis, ATP is made by
A. chemiosmosis. B. glycolysis. C. the Krebs cycle. D. the Calvin cycle. E. the passing of electrons from photosystem I to an electron transport chain.
In order for the scientists to artificially select Drosophila for their number of bristles,
In the laboratory, fruit flies (Drosophila) were artificially selected for the number of bristles on their bodies. One population (R) was selected for low numbers of bristles, a second population (S) for high numbers of bristles.
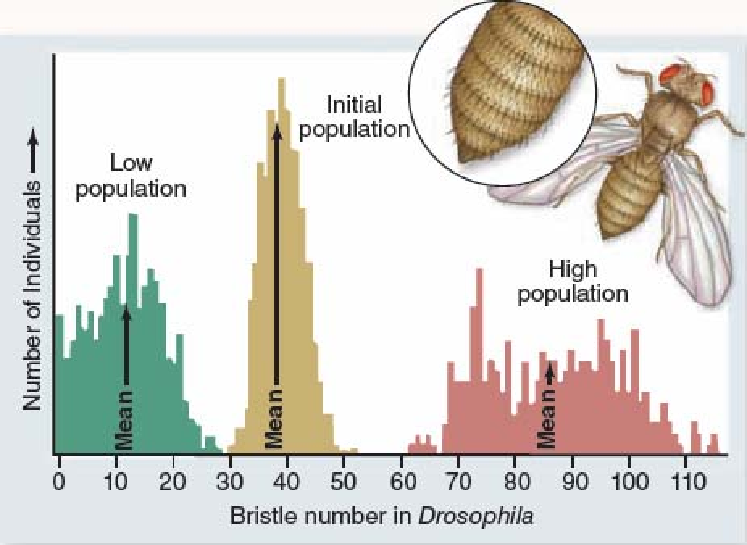
A. no change was seen; it's much too soon.
B. some slight increase of bristle numbers was already evident.
C. a vast, overlapping range of bristle numbers was seen.
D. a slight increase in bristles in S, a slight decrease in R, with a little overlap in the middle ranges.
E. a huge increase in S, a huge decrease in R, with no overlap whatsoever.
A(n) ________ trait will spread more quickly through a sexually reproducing population than a asexually reproducing one
a. adaptive b. neutral c. negative d. harmful e. deleterious