A firm is currently producing in the elastic portion of its demand curve. What course of action do you recommend for it assuming it wants to raise revenue?
A. Continue selling at the same price, but increase the amount it produces.
B. Increase price, because if it increases price and demand is elastic, total revenue will increase.
C. Continue producing at the current output level, because it maximizes its total revenue by producing in the elastic portion of its demand curve.
D. Reduce price, because if it reduces price and demand is elastic, total revenue will increase.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
A disagreement point is
A) an item of contention between the two bargaining players. B) a way of keeping score in a negotiation. C) the point in a negotiation where the players cannot reach an agreement. D) the outcome that occurs if there is no agreement in a bargain.
Figure 7-10
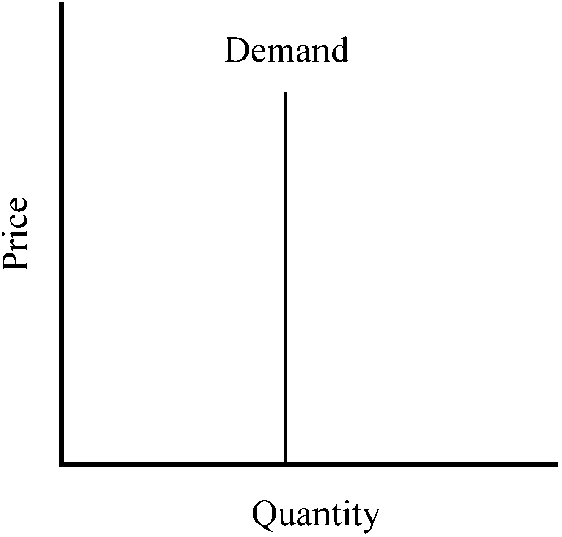
depicts a demand curve with a price elasticity that is
a.
unitary, implying that a percent change in price leads to an equal percent change in quantity demanded.
b.
perfectly inelastic, implying that the same amount will be purchased regardless of the price of the good.
c.
equal to zero.
d.
both b and c.
Suppose that a firm's legal staff concludes that a new production process that the firm is developing is patentable. Graphically, this new information would shift the firm's expected-rate- of-return curve on R&D to the:
A. right and reduce its optimal amount of R&D. B. right and increase its optimal amount of R&D. C. left and increase its optimal amount of R&D. D. left and reduce its optimal amount of R&D.
Other things being equal, as diminishing marginal returns begin to occur, the marginal revenue product of labor:
A. decreases as more workers are used. B. increases as more workers are used. C. remains unchanged as more workers are used. D. None of these