Which of the following quantities decrease in response to a tax on a good?
a. the equilibrium quantity in the market for the good, the effective price of the good paid by buyers, and consumer surplus
b. the equilibrium quantity in the market for the good, producer surplus, and the well-being of buyers of the good
c. the effective price received by sellers of the good, the wedge between the effective price paid by buyers and the effective price received by sellers, and consumer surplus
d. None of the above is necessarily correct unless we know whether the tax is levied on buyers or on sellers.
b
You might also like to view...
The table below shows the weekly supply for hamburgers in a market where there are just three sellers.PriceSeller 1 Qs 1Seller 2 Qs 2Seller 3 Qs 3$5854464334322221If the price of a hamburger increases from $2 to $4, then the weekly market quantity of hamburgers supplied will
A. increase from 5 to 13. B. decrease from 9 to 5. C. decrease from 13 to 5. D. increase from 5 to 9.
According to the table shown, when 5 units are produced:
This table shows the total costs for various levels of output for a firm operating in a perfectly competitive market.
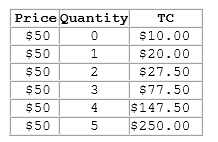
A. profits are maximized.
B. profits are positive.
C. the firm is producing less than the profit-maximizing amount.
D. the firm is producing more than the profit-maximizing amount.
More detailed financial instruments tend to be:
A. more costly because it will cost more to create. B. less costly because they can be standardized more easily. C. more desirable than less detailed ones, no matter what the price. D. less costly because all possible contingencies are covered.
An economy that is operating below its full-employment capacity is experiencing a(n):
A. tax-induced recession. B. recessionary gap. C. inflationary gap. D. market correction.