The diagram concerns supply adjustments to an increase in demand (D 1 to D 2 ) in the immediate market period, the short run, and the long run. In the immediate market period, the increase in demand will:
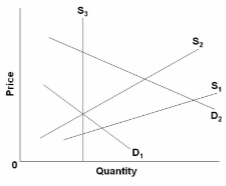
A. have no effect on either equilibrium price or quantity.
B. increase equilibrium price but not equilibrium quantity.
C. increase equilibrium quantity but not equilibrium price.
D. increase both equilibrium price and quantity.
B. increase equilibrium price but not equilibrium quantity.
You might also like to view...
Using the information in the table above, calculate the employment-to-population ratio
A) 75 percent B) 65 percent C) 50 percent D) 23.2 percent
If Joe and Sarah are faced with the game in the figure shown, we can see that:
This figure shows the payoffs involved when Sarah and Joe work on a school project together for a single grade. They both will enjoy a higher grade when more effort is put into the project, but they also get pleasure from goofing off and not working on the project. The payoffs can be thought of as the utility each would get from the effort they individually put forth and the grade they jointly receive.
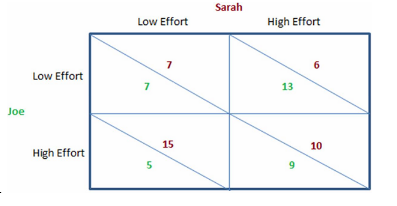
A. Joe has a dominant strategy, but Sarah does not.
B. Sarah has a dominant strategy, but Joe does not.
C. neither student has a dominant strategy.
D. both students have a dominant strategy.
What factors influence the stability of velocity? Why is velocity's stability a crucial issue for assessing the effectiveness of monetary policy?
One explanation economists offer to explain why a decline in the unemployment rate can raise the rate of inflation rates is that
a. firms will be put in a position of competing more intensely for scarce resources b. people will pay higher prices because competition among the suppliers—the firms—intensifies c. workers will focus more directly on protecting their jobs d. firms will refuse to shift higher labor costs along to consumers for fear of losing their markets e. more workers will drop out of the labor market