Suppose that an economy's labor productivity fell by 3 percent and its total worker-hours remained constant between year 1 and year 2. We could conclude that this economy's:
A. real GDP declined.
B. capital stock increased.
C. production possibilities curve shifted outward.
D. actual production moved from one point to another on a fixed production possibilities curve.
A. real GDP declined.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as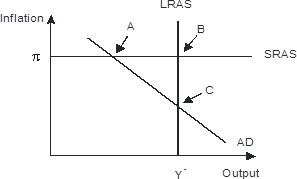
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward C. Aggregate demand shifting rightward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
What causes capital and labor shares of gross domestic product to remain consistent over the years?
What will be an ideal response?
One of the main differences between the recent economic history of the high-performance Asian economies and most of the rest of the world is that growth in the Asian economies
A) increased in the 1960s. B) continued in the 1980s. C) slowed down in the 1960s. D) slowed down in the 1980s. E) slowed down in the 1970s.
Most economists today believe that the Phillips curve is
a. vertical in the short run but downward sloping in the long run. b. upward sloping in the short run but vertical in the long run. c. downward sloping in the short run but vertical in the long run. d. vertical in the short run but upward sloping in the long run.