How does the social problem of positive externalities differ from the problem created by negative externalities?
A) Positive externalities can create free-rider problems; negative externalities do not.
B) Positive externalities are created by altruistic people; negative externalities are not.
C) Negative externalities can create free-rider problems; positive externalities do not.
D) Negative externalities are created by selfish people; positive externalities are not.
E) Trick question: neither positive nor negative externalities create a social problem.
A
You might also like to view...
The demand for labor reflects the point that the
A) lower the real wage rate, the greater the quantity of labor demanded. B) higher the real wage rate, the greater the quantity of labor demanded. C) nominal wage rate and not the real wage rate determines the quantity of labor demanded. D) real wage rate does not affect the quantity demanded of labor. E) demand for labor depends on the supply of labor.
In general we can note that households with lower wealth tend to have a ________ MPC relative to wealthier households.
A. similar B. lower C. exactly equivalent D. higher
According to the real business cycle theory, ________ are responsible for economic growth.
A. expansionary fiscal and monetary policies B. positive shifts in the AS curve C. positive shifts in the AD curve D. trade and income policies
Refer to the figures. Which of the following events would most likely result in higher unemployment?
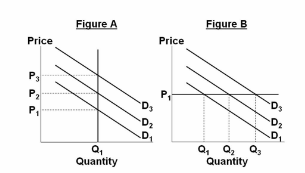
A. A shift from D 2 to D 1 in Figure A.
B. A shift from D 2 to D 3 in Figure A.
C. A shift from D 2 to D 1 in Figure B.
D. A shift from D 2 to D 3 in Figure B.