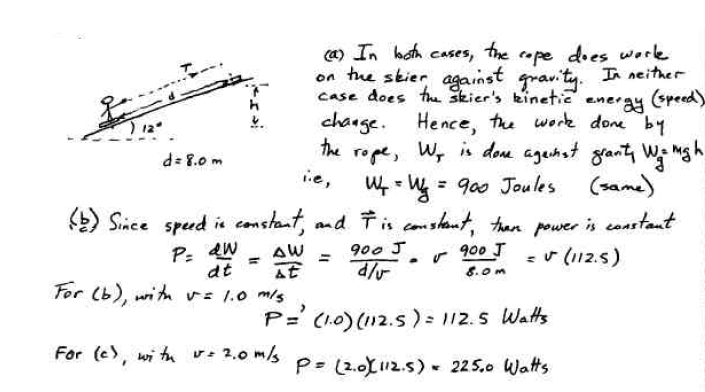
A skier is pulled by a tow rope up a frictionless ski slope that makes an angle of 12° with the horizontal. The rope moves parallel to the slope with a constant speed of 1.0 m/s. The force of the rope does 900 J of work on the skier as the skier moves a distance of 8.0 m up the incline.
(a) If the rope moved with a constant speed of 2.0 m/s, how much work would the force of the rope do on the skier as the skier moved a distance of 8.0 m up the incline? At what rate is the force of the rope doing work on the skier when the rope moves with a speed of
(b) 1.0 m/s and
(c) 2.0 m/s?
Answer:
You might also like to view...
The size of the smallest detail a microscope can resolve is
A. 1/1000 the wavelength of the light used B. Half the wavelength of the light used C. 10 times the wavelength of the light used D. Infinitely small.
At an instant when a particle of mass 50 g has an acceleration of 80 m/s2 in the positive x direction, a 75-g particle has an acceleration of 40 m/s2 in the positive y direction. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the center of mass of this two-particle system at this instant?
A. 60 m/s2 B. 56 m/s2 C. 40 m/s2 D. 50 m/s2 E. 46 m/s2
When an electron moves from the n = 1 to the n = 3 orbit:
a. the radius doubles and the angular momentum increases by a factor of 9. b. the radius increases by a factor of 9, and the angular momentum triples. c. both the radius and the angular momentum increase by a factor of 9. d. both the radius and the angular momentum triple.
A proton (mass = 1.67 × 10^-27 kg, charge = 1.60 × 10^-19 C) moves from point A to point B under the influence of an electrostatic force only. At point A the proton moves with a speed of 60 km/s. At point B the speed of the proton is 80 km/s. Determine the potential difference VB - VA
a. +15 V b. -15 V c. -33 V d. +33 V e. -20 V