When actions are finely divisible, the marginal benefit of action X is equal to:
A. the slope of a line that is tangent to the total benefit curve at X.
B. the slope of a line from the origin to a point on the total benefit curve at X.
C. the marginal cost of X.
D. the inverse of the slope of the total benefit curve at point X.
A. the slope of a line that is tangent to the total benefit curve at X.
You might also like to view...
What is a potential drawback of a high degree of redistribution and too much taxation of the wealthy?
a. Discouraging entrepreneurship b. Expanding political and federal power c. Creating a progressive tax system d. Triggering more offshoring of jobs
Up to what amount would a risk-neutral gambler pay to enter a game where on the flip of a fair coin, if you call the correct outcome the payoff is $2,000?
A. Up to $2,000. B. Up to $1,000. C. More than $1000 but less than $2000. D. More than $1,500.
Exhibit 7-12 Marginal revenue and cost per unit curves
?
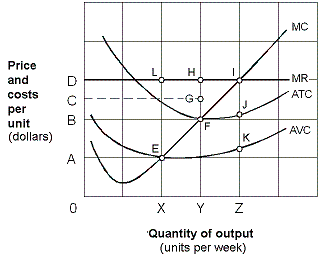
A. OZID. B. OYHD. C. OXLD. D. OYFB.
In the case study at the end of Chapter 20, Global Insurance is a company that offers disability insurance. Its major problem is that it does not process policies very quickly, largely because it is not computerized and the process is not linked electronically. The CEO wishes to innovate and to change organizational architecture to computerize and link all phases of the application process. What aspects of leadership need to be emphasized during this difficult transition at Global?
What will be an ideal response?