Reflects sunlight at leaf surface.
Choose the letter of the best match:
A. abscisic acid
B. trichomes
C. aquaporin
D. endodermis
E. stoma
B. trichomes
You might also like to view...
The mechanisms by which the body of a plant functions in its environment is the ____ of the plant
a. morphology b. ecology c. anatomy d. distribution e. physiology
Which of the following is an appropriate interpretation for these graphs?
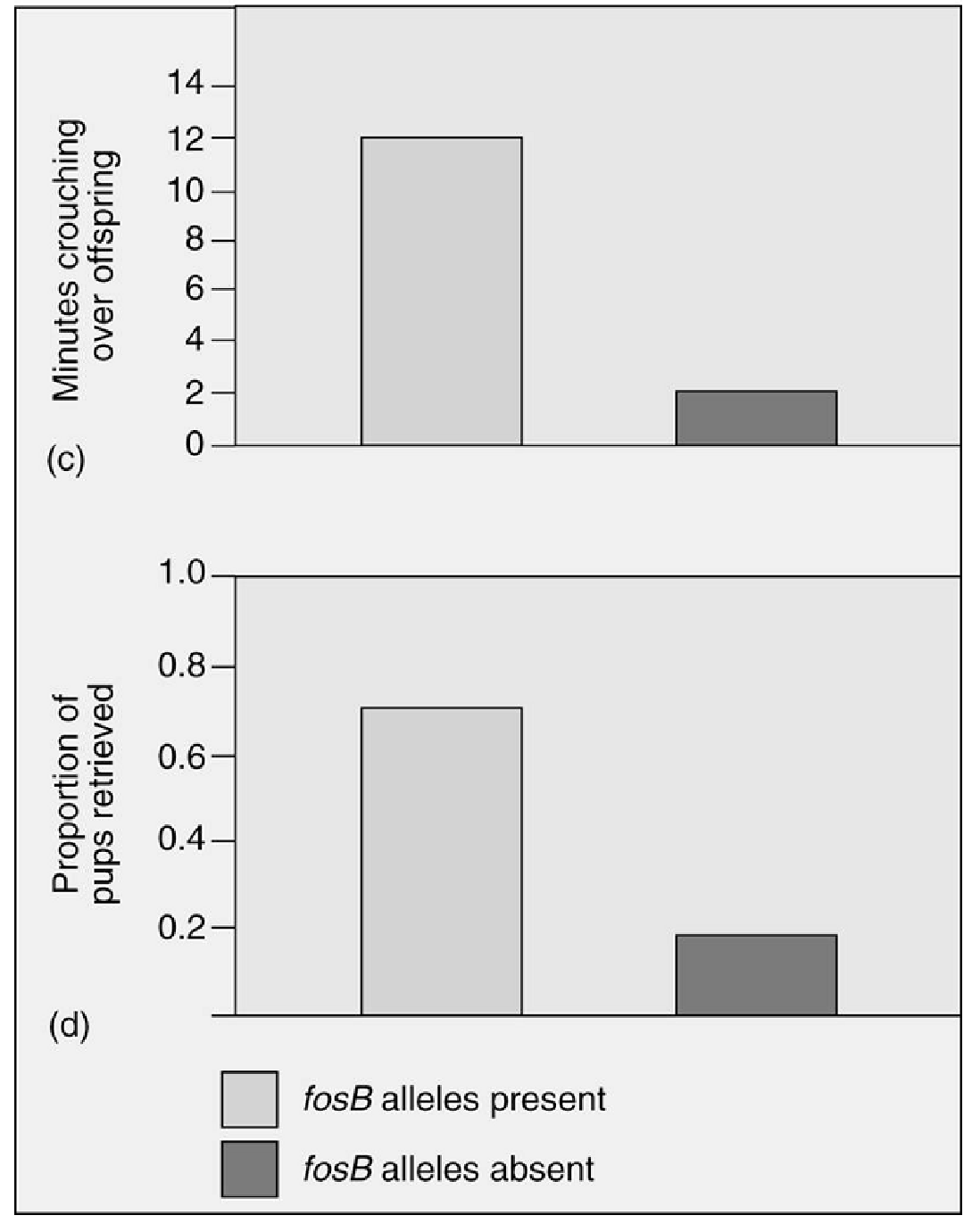
Maternal care (as measured by minutes crouching over offspring and proportion of pups retrieved) in female mice that have the fosB allele is
A. less than the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele.
B. greater than the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele.
C. the same as the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele.
D. less than the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele; however, the graphs depict only minor differences, which are most likely not significant.
E. not possible to determine from the data.
Clarify question:
What is the key concept addressed by the question?
What type of thinking is required?
Gather Content:
What do you already know about the relationship between maternal behavior and a particular allele? What other information is related to the question?
Choose Answer:
Given what you now know, what information is most likely to produce the correct answer?
Reflection on Process:
Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
Phase ________ trials occur when a drug is tested on individuals with a disease to determine the effectiveness of a drug in treating a disease
A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V
Which of the following diseases is NOT correctly matched to its reservoir?
A) tuberculosis — cattle B) histoplasmosis — soil C) psittacosis — parakeets D) coccidioidomycosis — air E) pneumocystis — humans