When network externalities are present, the market demand for the good in question becomes:
A.unit elastic.
B. less elastic.
C. more elastic.
D. perfectly inelastic.
C. more elastic.
You might also like to view...
The efficient quantity of output of a product with external costs of production is
A) where the demand curve and the producer's supply curve intersect. B) where the marginal social cost curve and marginal social benefit curve intersect. C) as low as possible. D) zero.
Mitt Romney argued in a debate with President Obama that the economy had grown more slowly in each year of the President's term than in the year prior to Obama’s presidency. This claim is most related to the field of:
A. microeconomics. B. public policy. C. macroeconomics. D. financial economics.
Suppose a monopolist chooses to advertise its good and its own demand curve shifts to the right, then we know that
a. the industry's demand curve shifts in precisely the same way b. its competitors share some of the benefits of the advertising c. the monopolist's cost curves will shift to accommodate the shift in demand d. the price of substitute goods will fall e. consumers are turned off by the advertising and buy less at every price
Refer to the graphs shown, which depict a perfectly competitive market and firm. If market demand decreases from D0 to D1: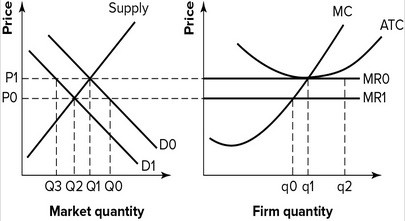
A. market price remains at P0 because perfectly competitive firms can't earn positive economic profit. B. the firm's output remains at q1 because perfectly competitive firms can't earn positive economic profit. C. market price falls from P0 to P1 and the firm's output rises from q0 to q1. D. market price falls from P0 to P1 and the firm's output falls from q1 to q0.