Refer to the diagram in which S is the market supply curve and S 1 is a supply curve comprising all costs of production, including external costs. Assume that the number of peopleaffected by these external costs is large. If the government wishes to
establish an optimal allocation of resources in this market, it should:
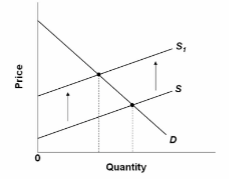
A. not intervene because the market outcome is optimal.
B. subsidize consumers so that the market demand curve shifts leftward.
C. subsidize producers so that the market supply curve shifts leftward (upward).
D. tax producers so that the market supply curve shifts leftward (upward).
D. tax producers so that the market supply curve shifts leftward (upward).
You might also like to view...
In the aggregate expenditures diagram, the 45° line represents the equilibrium condition that
A. Y* = Y. B. AE = C + I + G + NX. C. I = C. D. Y = AE.
The major similarity between a monopolist and a monopolistically competitive firm is that:
a. both are price takers. b. both face a horizontal demand curve. c. both are the sole producers of a particular good. d. both face a negatively sloped demand curve. e. both are affected by the decision of their rivals.
What's the difference between firm-specific risk and market risk? Will diversification eliminate one or both? Explain
The sticky-price theory of the short-run aggregate supply curve says that if the price level rises by 5% and people were expecting it to rise by 2%, then firms have
a. higher than desired prices, which leads to an increase in the aggregate quantity of goods and services supplied. b. higher than desired prices, which leads to a decrease in the aggregate quantity of goods and services supplied. c. lower than desired prices, which leads to an increase in the aggregate quantity of goods and services supplied. d. lower than desired prices, which leads to a decrease in the aggregate quantity of goods and services supplied.