The long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve is a ________ drawn at ________
a. horizontal line; the equilibrium price level
b. vertical line; the potential output level
c. downward-sloping curve; the equilibrium price level
d. horizontal line; the potential output level
b
You might also like to view...
Refer to Exhibit 6-3. What is the random variable in this experiment?
a. the weight of football players b. 200 pounds c. 25 pounds d. the normal distribution
Because the smallcountry monopolist loses the ability to control the market price, consumers enjoy more quantity, competitive prices, and:
a. a bonus because the foreign goods are of higher quality. b. a loss because the monopoly loses profits. c. higher consumer surplus because the monopolist's producer surplus is reduced. d. a loss because now unions have less power than before.
Where does the point of equilibrium fall on this graph?
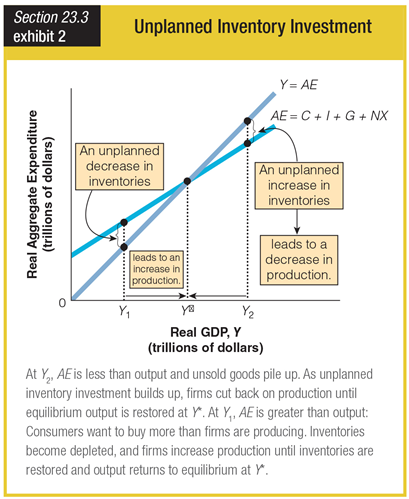
a. at Y1 on the line marked Y = AE
b. at Y2 on the line marked AE = C + I + G + NX
c. at Y* where the two lines intersect
d. nowhere
Which of the following statements is NOT true about using per capita real GDP to measure a nation's economic growth?
A. The definition assumes that some of the increase in productivity goes to the poor. B. The definition does not indicate how the increase in growth is being disturbed among the nation's population. C. The definition has understated actual economic growth because it does not take into consideration changes in leisure. D. The definition is not perfect for measuring increases in a nation's productive capacity.