The types of goods Japan exports and imports appear to be well explained by
A) Japanese endowments of factors of production (e.g. land, labor, capital, natural resources).
B) high and rising Japanese tariffs.
C) advertising and other sales promotion efforts.
D) All of the above.
A
You might also like to view...
The payoff matrix below shows the daily profit for two firms, Row Restaurant and Column Cafe, for two different strategies, publishing coupons in the student paper and not publishing coupons in the student paper.  If Row Restaurant publishes coupons, Column Cafe would earn the highest profit if it:
If Row Restaurant publishes coupons, Column Cafe would earn the highest profit if it:
A. only offered coupons half of the time. B. also published coupons. C. did not publish coupons. D. chooses either strategy because Column Cafe will have the same profit in either case.
If the production of a particular good involves significant external benefits, to force the externality to be internalized the government might:
a. impose a tax on production of the good in order to increase production. b. impose a tax on production of the good in order to decrease production. c. offer a subsidy for production of the good in order to increase production. d. offer a subsidy for production of the good in order to decrease production.
?Hair Pins /hourBandanas /hourNigel410Mia93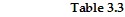 Consider two individuals, Nigel and Mia, who produce hair pins and bandanas. Nigel's and Mia's hourly productivity are shown in Table 3.3. Nigel's opportunity cost of producing one bandana is:
Consider two individuals, Nigel and Mia, who produce hair pins and bandanas. Nigel's and Mia's hourly productivity are shown in Table 3.3. Nigel's opportunity cost of producing one bandana is:
A. 1/4 of a hair pin. B. 2/5 of a hair pin. C. 2.5 hair pins. D. 4 hair pins.
If a country increased the production of its capital goods, then
A. the more unemployed resources there will be in the future. B. the more consumption of goods we can have today. C. the more unemployed resources there are today. D. the less consumption we can have today, but we will have more in the future.