If equilibrium level of real Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
is less than the full-employment real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) consistent with the position of the economy's long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve, then the difference between full-employment real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and current equilibrium real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is
A) an aggregate demand shock.
B) an aggregate supply shock.
C) a recessionary gap.
D) an inflationary gap.
C
You might also like to view...
According to the classical system, saving is a function of
a. income. b. the real interest rate. c. the real wage. d. the profitability of firms. e. all of the above.
If total consumption is $5 billion, investments $2 billion, government purchases $1 billion, exports $1 billion, and imports $3 billion, the GDP must equal:
A. $6 billion. B. $12 billion. C. $9 billion. D. $3 billion.
The change in the money supply in an economy is measured as:
a. the difference between the government deficit and government borrowing. b. the sum of a change in high-powered money and the change in tax revenues. c. the difference between government borrowing and government spending. d. the ratio of the change in excess reserves to the deposit expansion multiplier. e. the change in the government budget deficit.
At which point in Figure 9-7 would a perfectly competitive firm earn the same profit, or suffer the same loss, by producing rather than by shutting down?
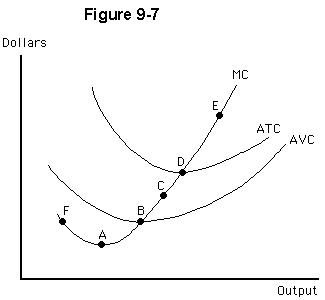
a.
A
b.
B
c.
C
d.
D
e.
F