A coaxial cable has an inner cylindrical conductor surrounded by cylindrical insulation and an outer cylindrical conducting shell. The outer shell carries the same current but in the opposite direction from that in the inner conductor as shown. If the coaxial cable sits in a uniform magnetic field directed upwards with respect to the cable, the effect of the field on the cable is
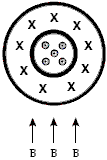
a.
a net force to the left.
b.
a net force to the right.
c.
a net force upwards.
d.
no net force but a slight shift of the inner conductor to the left and the outer conductor to the right.
e.
no net force but a slight shift of the inner conductor to the right and the outer conductor to the left.
d
You might also like to view...
The inside of a house is at 20°C on an early morning when the temperature outside is 15°C. The next morning the inside temperature is the same but the outside temperature is now 10°C. How much does the energy per unit time lost by conduction through the walls, windows, doors, etc., change for the house from the first morning to the second one?
a. Since the inside temperature stays the same, the loss is the same both days. b. The loss doubles. c. The loss halves. d. The loss increases by 5/288 since we need to use the Kelvin scale for this calculation.
If all people, animals, trains and trucks all over the world began to walk or run towards the east (opposite the direction of Earth's spin), then
A) Earth would spin a bit faster. B) Earth would spin a bit slower. C) Earth's spin would not be affected at all.
When objects at different temperatures are brought into thermal contact with one another, the resulting spontaneous flow of heat proceeds from the object with the higher
A) thermal conductivity to the one with the lower thermal conductivity. B) specific heat to the one with the lower specific heat. C) heat capacity to the one with the lower capacity. D) temperature to the one with the lower temperature. E) impossible to predict on the basis of this data.
A wheel (radius = 0.20 m) starts from rest and rotates with a constant angular acceleration of 2.0 rad/s2 . At the instant when the angular velocity is equal to 1.2 rad/s, what is the magnitude of the total linear acceleration of a point on the rim of the wheel?
a. 0.40 m/s2 b. 0.29 m/s2 c. 0.69 m/s2 d. 0.49 m/s2 e. 0.35 m/s2